误差分析是A-level各大考试局必考内容,涉及的考点有precision(精度)和accuracy(准确性),两种error(误差),如何减下误差,还有uncertainty(不确定度)和percentage uncertainty的计算。本文只讨论一些涉及误差的定性分析,不讨论不确定度的计算。
Part A. Precision and Accuracy
Precision:the size of the smallest division (on the measuring instrument)
Accuracy:how close measured value is to the true value
从实验测量的角度来看,precision指的是测量仪器的最小刻度,最小刻度越小仪器精度越高。例如micrometer:0.01mm,meter rule:1mm,还有就是vernier calipers在A-level中一般是0.1mm的精度,如果是digital vernier calipers则是0.01mm,所以micrometer 和 digital vernier calipers的精度在这几个仪器中最高。而accuracy侧重的是测量值与真实值之间的接近程度,测量值越接近真实值就越accurate。
Example 1
A school has a piece of aluminium that it uses for radioactivity experiments. Its thickness is marked as 3.2 mm. A student decides to check this value. He has vernier calipers which give measurements to 0.1 mm and a micrometer which gives measurements to 0.01 mm.
Which statement must be correct?
A. The micrometer gives a more accurate measurement.
B. The micrometer gives a more precise measurement.
C. The vernier calipers give a more accurate measurement.
D. The vernier calipers give a more precise measurement.
分析:题目给了铝片上的刻度,要检查该刻度的准确性,所以不知道真实值是多少,无法判断两个测量值谁更accurate。而micrometer的精度是0.01mm,vernier calipers的精度是0.1mm,so micrometer is more precise。
Example 2
A voltage is carefully measured with a high-quality instrument and found to be 2.321V.
Two students, using two different methods, conclude that the voltage is 2.33V and 2.344V respectively.
Which statement is correct?
A. 2.33V is less accurate and less precise than 2.344V.
B. 2.33V is less accurate and more precise than 2.344V.
C.2.33V is more accurate and less precise than 2.344V.
D. 2.33V is more accurate and more precise than 2.344V.
分析:题目首先给出一个通过高质量仪器细心测出的数值,这个值可认为非常接近真实值。后面给的两个数值,可以根据读数判断精度,2.33V的精度是0.01V,2.334V的精度是0.001V,所以2.334V is more precise。然后比较两个读数与2.321V的差值,差值较小的more accurate。
Part B. Systematic Errors and Random Errors
Systematic Errors:the reading is larger or small than (or varying from) the true reading by a constant amout
Random Errors:scatter in readings about the true reading
系统误差指的是测量值和真实值之间有恒定的差值,常见的有zero error or wrongly calibrated scale,即零误差或是仪器刻度有问题。比如在使用电子秤的时候没有回零,那么后面在该电子秤上的测量都会偏大或偏小一个恒定的差值。避免这种系统误差只需要在实验之前check zero errors。仪器刻度导致的系统误差需要更换仪器。
随机误差指的是读数在真实值附近分散排布,有比真实值大的读数,也有比真实值小的。最常见的是reading scale from different angles or wrongly interpolating between scale readings/divisions。对于随机误差,take several readings and take average可以减小。
Example 3
Four possible sources of error in a series of measurements are listed.
1. an analogue meter whose scale is read from different angles
2. a meter which always measures 5% too high
3. a meter with a needle that is not frictionless, so the needle sometimes sticks slightly
4. a meter with a zero error
Which errors are random and which are systematic?
|
random error |
systematic error |
A |
1 and 2 |
3 and 4 |
B |
1 and 3 |
2 and 4 |
C |
2 and 4 |
1 and 3 |
D |
3 and 4 |
1 and 2 |
分析:
1.由于从不同角度读数,可能导致读数分散在真实值附近,为random errors,
2.从always可以看出读数总是偏大5%,为systematic errors,3.从sometimes可以看出读数只是有时候会有问题,为random errors,4是最常见的systematic errors。
Example 4
A voltmeter gives readings that are larger than the true values and has a systematic error that varies with voltage.
Which graph shows the calibration curve for the voltmeter?
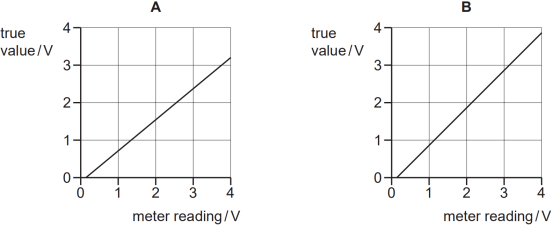
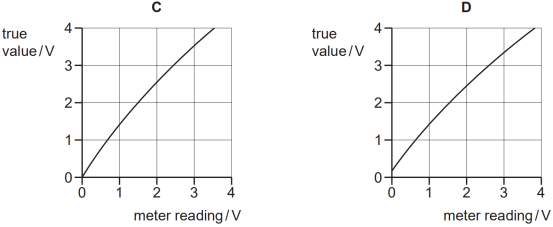
分析:本题通过图像来给出测量值和真实值,横轴表示仪器读数,纵轴表示真实值,如果图像是一条斜率为1且经过原点的直线,则表示测量值等于真实值。题干要求仪器读数大于真实值,所以图像得向右下方移动,所以C,D均不满足,题干还要求系统误差随着读数变化,B图斜率为1,同时图像向右下方移动,所以B图中的读数比真实值大,但相差的值恒定,并没有随着读数在变化,A图的斜率不等于1,所以A图的系统误差会随着读数变化。因此本题选A。本题有些同学觉得A选项不满足系统误差定义中提到的真实值和测量值之间有恒定的差值,实际上真实值和测量值之间如果有恒定的percentage uncertainty,就会出现随着测量值的变化差值也发生变化的情况,所以在理解系统误差时,这里的恒定的差值可以是一个恒定的数值,也可以是恒定的percentage uncertainty。
Example 5
The measurement of a particular time interval is repeated many times. The readings are found to vary. The results are shown in Fig. 1.1.
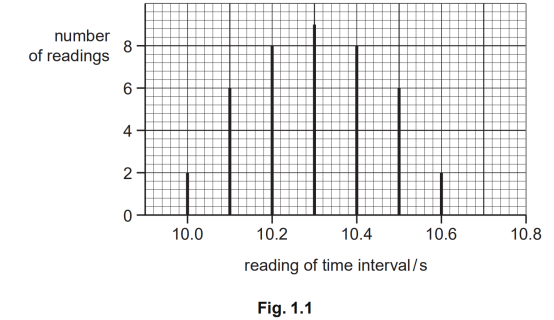
The true value of the time interval is 10.1 s.
(i) State how the readings on Fig. 1.1 show the presence of
1. a systematic error,
2. a random error.
(ii) State the expected changes to Fig. 1.1 for experimental measurements that are
1. more accurate,
2. more precise.
分析:本题是对前面几个概念的综合考查,在分析这种问题时,还需要有信息的提取能力。通过前面的学习有同学可能觉得系统误差和随机误差是对立的,二者只能存其一,所以对于这类题不知道怎么处理。解决这类题要紧扣定义。首先随机误差的依据是很容易发现的,即这幅图中的数据既有大于真实值的读数,也有小于真实值的读数,所以读数是分散在真实值附近的,random error: values are scattered。而系统误差就很难找了,主要是测量值有比真实值大的,也有小于真实值的。所以这种情况通常需要拿某些特殊值与真实值进行比较,比如把出现次数最多的读数peak与真实值相比,总是恒大于真实值,systematic error :peak is not the true value。
同样的在回答accurate时,也是看峰值比较靠近真实值,即 peak value moves towards the true value。而precise则是整体数据比较集中,即 lines are closer together / sharper peak。所以回答这类问题就是先紧扣定义,然后在题中找支持依据。
Part C. 误差对准确性和精度的影响
根据两种误差的定义,systematic errors会导致读数与真实值之间有差值,而accurate是测量值和真实值之间越接近则越准确,所以systematic errors会降低准确性。而precise则是强调的测量值之间的分散程度,对准确性没要求,所以只要仪器的精度高,分散度就会小。
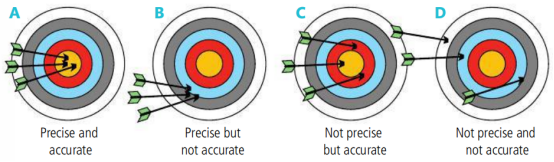
这幅图可以帮助我们更好的理解,
A图,箭都在靶心且很集中,所以既有准确性,精度也高,这种情况系统误差和随机误差都很小。
B图,箭很集中,但都偏离靶心,属于有精度,但不准确,这种通常是由于系统误差较大导致的,而随机误差很小。
C图,箭不集中,但在靶心附近,甚至有打在靶心上的,属于有准确性,但精度不高,这种通常随机误差较大,但系统误差较小。
D图,箭既不集中,又偏离靶心,属于既没准确性,精度又不高,这种两种误差都大。
Example 6
An ammeter has a zero offset error. This fault will affect
A. neither the precision nor the accuracy of the readings.
B. only the precision of the readings.
C. only the accuracy of the readings.
D. both the precision and the accuracy of the readings.
分析:零误差属于系统误差,所以读数会偏离真实值,影响准确性,而精度取决于仪器的最小刻度,零误差对精度没影响,因此本题选C。

